Unlock MCU ATMEGA2561 Heximal
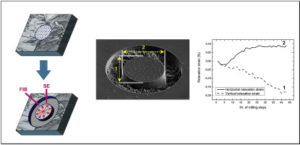
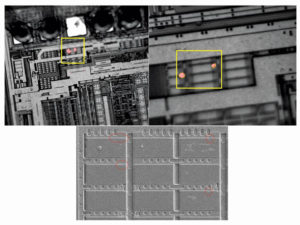
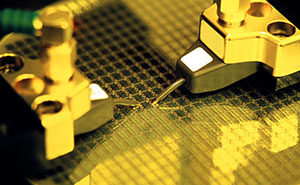
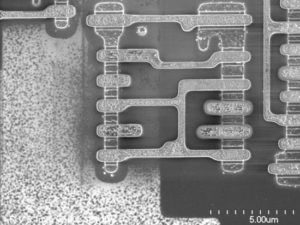
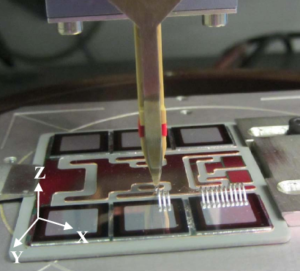
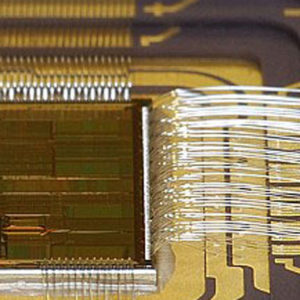
Unlock MCU ATMEGA2561 and extract Microcontroller ATmega2561 Heximal out from the memory include flash and eeprom, the program and data will be integrated as a united firmware after break Microcomputer ATmega2561 security fuse bit by focus ion beam technology;

Unlock MCU ATMEGA2561 and extract Microcontroller ATmega2561 Heximal out from the memory include flash and eeprom, the program and data will be integrated as a united firmware after break Microcomputer ATmega2561 security fuse bit by focus ion beam technology
The ATmega2561 AVR is supported with a full suite of program and system development tools including: C compilers, macro assemblers, program debugger/simulators, in-circuit emulators, and evaluation kits when chip PIC16C621 program reading.
Each device in the ATmega2561 family differs only in memory size and number of pins. Table 1 summarizes the different configurations for the six devices if microcontroller pic16c620 code reading.
Port A is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port A output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability.
As inputs, Port A pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running.
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability. As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated.
The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running. Port B has better driving capabilities than the other ports if MCU PIC16C622A software unlocking.
Port C is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port C output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability. As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port C pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running.
Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The Port D output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source capability.
As inputs, Port D pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up resistors are activated. The Port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active, even if the clock is not running.
Tags: unlock mcu archive,unlock mcu bin,unlock mcu code,unlock mcu content,unlock mcu data,unlock mcu eeprom,unlock mcu file,unlock mcu firmware,unlock mcu hex,unlock mcu information,unlock mcu memory,unlock mcu program