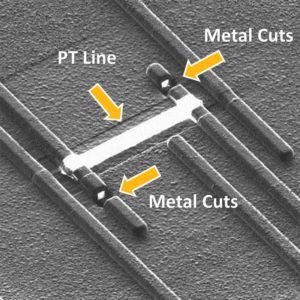
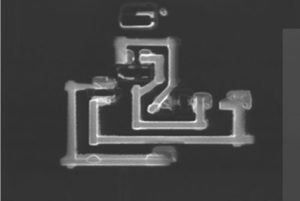
Unlock MCU ATmega1284A Heximal
Unlock MCU ATmega1284A Heximal from the encrypted flash memory and eeprom memory, reset the status of Microcontroller from locked to unlocked;
If ADC2 is selected as both the positive and negative input to the differential gain amplifier (ADC2 – ADC2), the remaining offset in the gain stage and conversion circuitry can be measured directly as the result of the conversion.
This figure can be subtracted from subsequent conversions with the same gain setting to reduce offset error to below 1 LSB. The ADC can operate in two modes – Single Conversion and Free Running.
In Single Conversion mode, each conversion will have to be initiated by the user. In Free Running mode, the ADC is constantly sampling and updating the ADC Data Register. The ADFR bit in ADCSR selects between the two available modes.
The ADC is enabled by setting the ADC Enable bit, ADEN in ADCSR. Voltage reference and input channel selections will not go into effect until ADEN is set. The ADC does not consume power when ADEN is cleared, so it is recommended to switch off the ADC before entering Power-saving sleep modes.
A conversion is started by writing a logical “1” to the ADC Start Conversion bit, ADSC. This bit stays high as long as the conversion is in progress and will be set to zero by hardware when the conversion is completed.
If a different data channel is selected while a conversion is in progress, the ADC will finish the current conversion before performing the channel change.
The ADC generates a 10-bit result, which is presented in the ADC data registers, ADCH and ADCL. By default, the result is presented right-adjusted, but can optionally be presented left-adjusted by setting the ADLAR bit in ADMUX.
Tags: unlock mcu locked archive,unlock mcu locked code,unlock mcu locked content,unlock mcu locked data,unlock mcu locked eeprom,unlock mcu locked file,unlock mcu locked firmware,unlock mcu locked information,unlock mcu locked memory,unlock mcu locked program