Retrieve Microcntroller IC ATmega8L-8PU
Retrieve Microcntroller IC Atmega8L-8PU memory program and the file format will be in binary or heximal:
The Atmega8L-8PU is a popular microcontroller, renowned for its balance of performance, low power consumption, and versatility in various embedded applications. In many projects, it plays a critical role in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial control environments. However, when the need arises to retrieve the microcontroller’s internal data or firmware, professionals are faced with a range of technological and technical challenges.
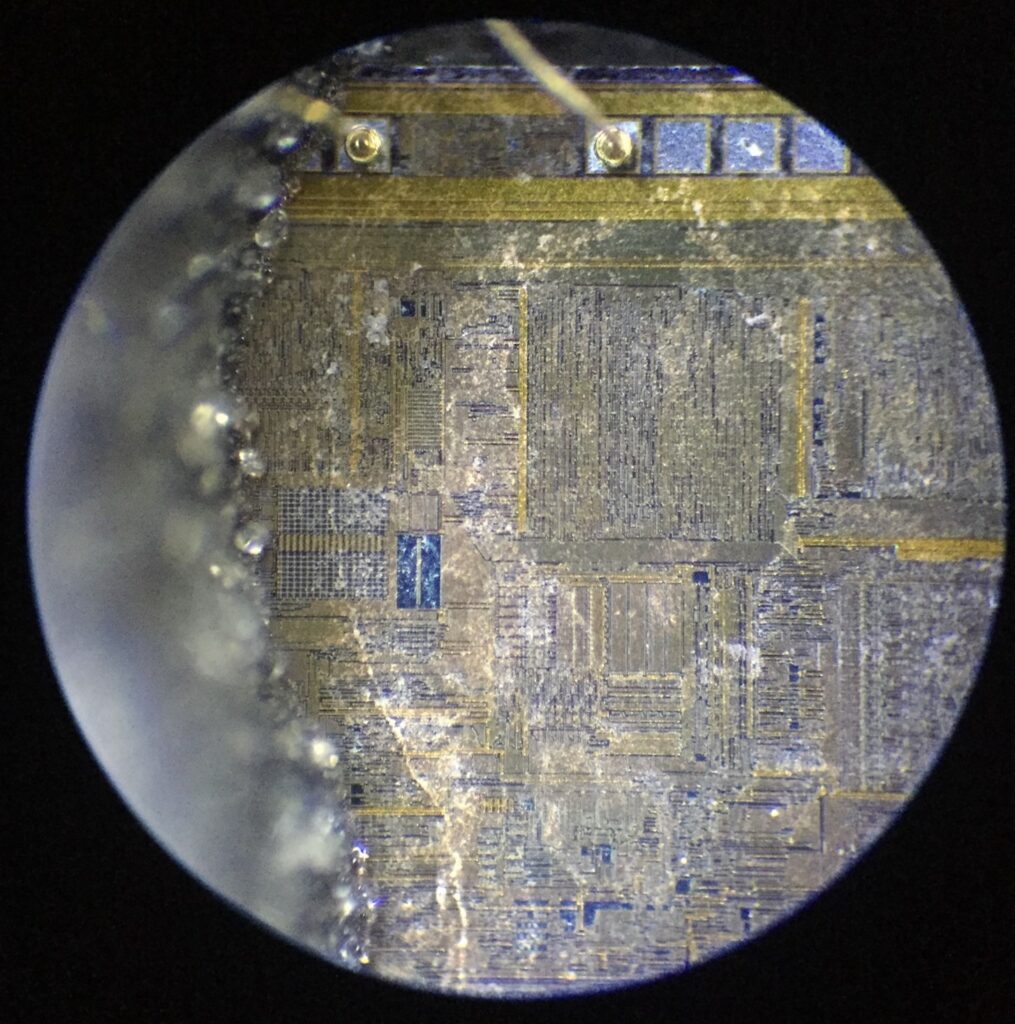
The process to retrieve data from the Atmega8L-8PU involves working with an integrated circuit designed with built-in security features that protect its stored program and memory contents. The security mechanisms are intended to prevent unauthorized access and to safeguard intellectual property. Such protection is beneficial in preventing malicious tampering but can present significant hurdles when legitimate recovery is necessary—whether due to accidental loss of original firmware, system failure, or legacy system maintenance.
One of the key challenges in retrieving the Atmega8L-8PU lies in its encrypted and secured memory structure. The microcontroller incorporates measures that render direct access to the stored firmware, calibration data, and configuration parameters extremely difficult. This secured design means that conventional debugging or programming tools often cannot access the internal memory without triggering protective protocols. Additionally, the integration of tamper detection features increases the risk of data loss if improper recovery methods are attempted.
Furthermore, retrieving data from the Atmega8L-8PU demands specialized equipment and a deep understanding of embedded systems. The technology behind these devices continuously evolves, necessitating that engineers and technicians stay updated with the latest tools and techniques to handle data recovery effectively. The complexity of the microcontroller’s architecture also means that even when partial data is successfully extracted, reconstructing the complete program or system configuration can be an intricate task.
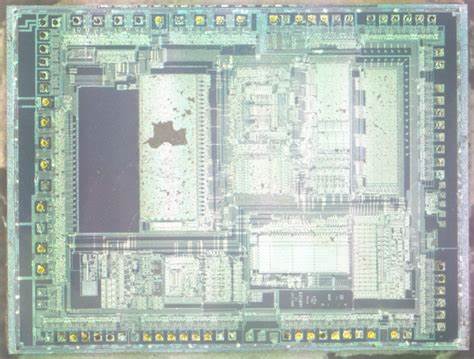
In conclusion, while the Atmega8L-8PU remains a robust choice for many modern applications, retrieving its stored data is a challenging endeavor. The secured design that protects its firmware and internal data ensures reliability during operation but complicates recovery efforts when issues arise. As a result, any attempt to retrieve data from this microcontroller must be approached with caution, a thorough understanding of its architecture, and strict adherence to legal and ethical standards.
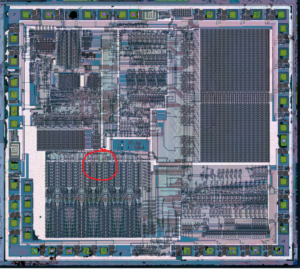
– Two 8-bit Timer/Counters with Separate Prescaler, one Compare Mode
– One 16-bit Timer/Counter with Separate Prescaler, Compare Mode, and Capture Mode
– Real Time Counter with Separate Oscillator
– 8-channel ADC in TQFP and QFN/MLF package
Eight Channels 10-bit Accuracy
– 6-channel ADC in PDIP package
Six Channels 10-bit Accuracy
– Byte-oriented Two-wire Serial Interface
– Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface
– Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chip Oscillator
– On-chip Analog Comparator
Special Microcontroller Features
– Power-on Reset and Programmable Brown-out Detection
– Internal Calibrated RC Oscillator
– External and Internal Interrupt Sources
– Five Sleep Modes: Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power-save, Power-down, and Standby I/O and Packages
– 23 Programmable I/O Lines
– 28-lead PDIP, 32-lead TQFP, and 32-pad QFN/MLF Operating Voltages
– 2.7 – 5.5V (ATmega8L)
– 4.5 – 5.5V (ATmega8) Speed Grades
– 0 – 8 MHz (ATmega8L)
Power Consumption at 4 Mhz, 3V, 25°C
– Active: 3.6 mA
– Idle Mode: 1.0 mA
– Power-down Mode: 0.5 µA

