Philip Microcontroller P89V51RD2 Flash Code Copying
Philip Microcontroller P89V51RD2 Flash Code Copying can reset power-on code execution, At initial power up, the port pins will be in a random state until the oscillator has started and the internal reset algorithm has weakly pulled all pins high.
Powering up the device without a valid reset could cause the MCU to start executing instructions from an indeterminate location. Such undefined states may inadvertently corrupt the code in the flash. A system reset will not affect the 1 kB of on-chip RAM while the device is running, however, the contents of the on-chip RAM during power up are indeterminate.
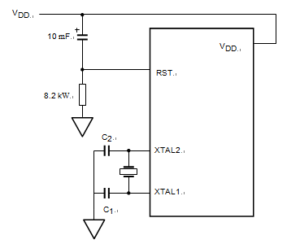
When power is applied to the device, the RST pin must be held high long enough for the oscillator to start up (usually several milliseconds for a low frequency crystal), in addition to two machine cycles for a valid power-on reset. An example of a method to extend the RST signal is to implement a RC circuit by connecting the RST pin to VDD through a 10 F capacitor and to VSS through an 8.2KW resistor as shown in below Figure.
Note that if an RC circuit is being used, provisions should be made to ensure the VDD rise time does not exceed 1 millisecond and the oscillator start-up time does not exceed 10 milliseconds. For a low frequency oscillator with slow start-up time the reset signal must be extended in order to account for the slow start-up time.
This method maintains the necessary relationship between VDD and RST to avoid programming at an indeterminate location, which may cause corruption in the code of the flash which has been acquired by NXP Chip P89LPC970 Heximal Code Dumping. The power-on detection is designed to work during initial power up, before the voltage reaches the brown-out detection level. The POF flag in the PCON register is set to indicate an initial power up condition. The POF flag will remain active until cleared by software.