NXP P89LPC925 Flash Binary Readout
Automatic Address Recognition is a feature which allows the UART to recognize certain addresses in the serial bit stream by using hardware to make NXP P89LPC925 Flash Binary Readout.
This feature saves a great deal of software overhead by eliminating the need for the software to examine every serial address which passes by the serial port. This feature is enabled for the UART by setting the SM2 bit in SCON.
In the 9 bit UART modes, mode 2 and mode 3, the Receive Interrupt flag (RI) will be automatically set when the received byte contains either the ‘Given’ address or the ‘Broadcast’ address. The 9 bit mode requires that the 9th information bit is a ‘1’ to indicate that the received information is an address and not data.
Using the Automatic Address Recognition feature allows a master to selectively communicate with one or more slaves by invoking the Given slave address or addresses. All of the slaves may be contacted by using the Broadcast address to Crack Microcontroller P89C669 Eeprom Memory. Two Special Function Registers are used to define the slave’s address, SADDR, and the address mask, SADEN. SADEN is used to define which bits in the SADDR are to be used and which bits are ‘don’t care’.
The SADEN mask can be logically ANDed with the SADDR to create the ‘Given’ address which the master will use for addressing each of the slaves. Use of the Given address allows multiple slaves to be recognized while excluding others. This device uses the methods presented in below Figure to determine if a ‘Given’ or ‘Broadcast’ address has been received or not.
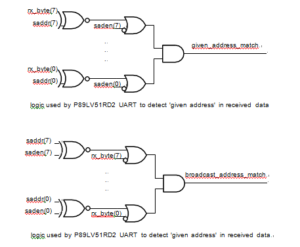
Schemes used by the UART to detect ‘given’ and ‘broadcast’ addresses when multiprocessor communications


