NXP MC908GT8 Program Cloning
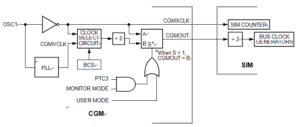
The bus clock generator provides system clock signals for the CPU and peripherals on the MCU which is quite useful for NXP MC908GT8 Program Cloning. The system clocks are generated from an incoming clock, CGMOUT, as shown in below Figure. This clock can come from either an external oscillator or from the on-chip PLL.
In user mode, the internal bus frequency is either the crystal oscillator output (CGMXCLK) divided by four or the PLL output (CGMVCLK) divided by four.
When the power-on reset module or the low-voltage inhibit module generates a reset, the clocks to the CPU and peripherals are inactive and held in an inactive phase until after the 4096 CGMXCLK cycle POR timeout has been completed to faciliate the process of Pull Microcontroller Chip Motorola MC68HC11A0FN3. The RST pin is driven low by the SIM during this entire period. The IBUS clocks start upon completion of the timeout.
Upon exit from stop mode (by an interrupt, break, or reset), the SIM allows CGMXCLK to clock the SIM counter. The CPU and peripheral clocks do not become active until after the stop delay timeout. This timeout is selectable as 4096 or 32 CGMXCLK cycles from MCU RECOVERING.
In wait mode, the CPU clocks are inactive. The SIM also produces two sets of clocks for other modules. Refer to the wait mode subsection of each module to see if the module is active or inactive in wait mode in order to Crack Microprocessor IC Freescale MC9S12XDG128. Some modules can be programmed to be active in wait mode.