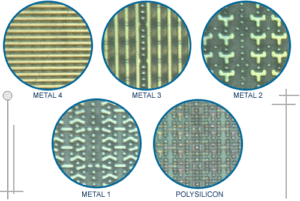
Microcontroller Reverse Engineering
Through the legislative history of Microcontroller Reverse Engineering, it can be known that the legitimacy of reverse engineering is recognized in the law as a defense of infringement. First of all, because there is a traditional “second source of supply” in the semiconductor industry for a long time,
Secondly, because Microcontroller Reverse Engineering can promote the development of the entire secured microcontroller industry, by allowing competitors to analyze and research existing microcontroller layout designs, it is easier and faster to produce integrated circuit with similar performance but more advanced technology.
However, accompany with the benefit microcontroller reverse engineering come with, it also brings certain drawbacks, which is easy to cause litigation disputes in practice. Because the reverse engineering is to create the second layout design based on the analysis and evaluation of the first layout design, the second layout design will inevitably have the same and similarities with the first layout design, so it is very easy to have confusion with Copying infringement and leads to controversy.
Copying the layout design through PIC MCU Reverse Engineering without the consent of the right holder constitutes an infringement. There are two main types of microcontroller copying here, one is full replication and the other is partial replication.