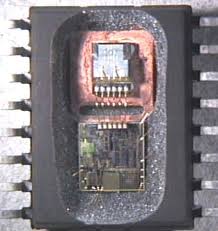
MCU STM32F100VC Flash Program Unlocking
MCU STM32F100VC flash program unlocking involves the process of cracking and decoding the secured and encrypted firmware stored within its flash memory and EEPROM memory. The STM32F100VC microcontroller (MCU) is designed with protective mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to its binary, heximal, and program data. However, through advanced reverse engineering techniques, it’s possible to unlock the locked firmware and retrieve the embedded software and source code.
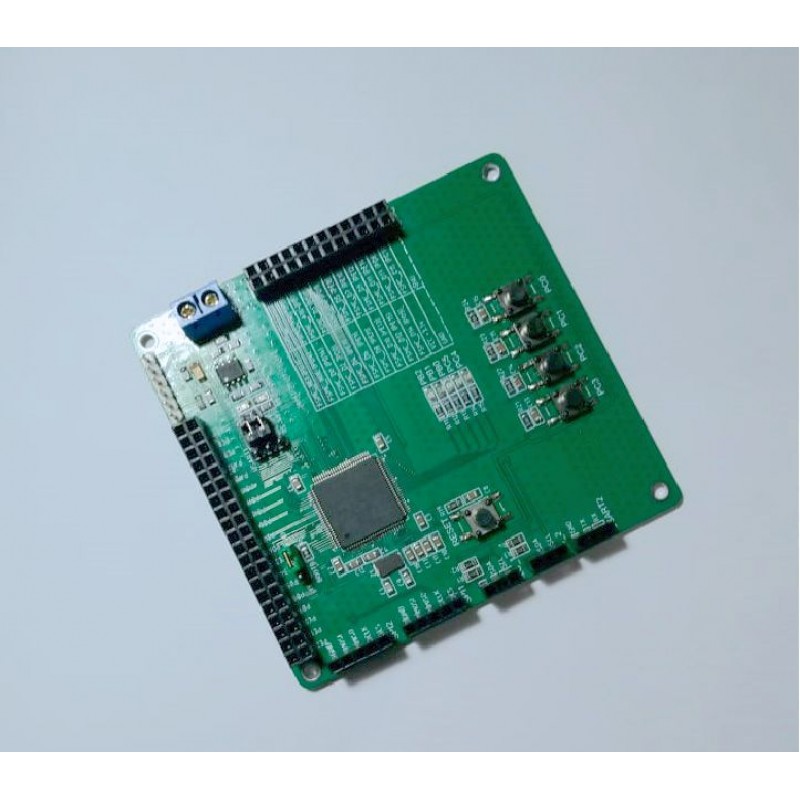

The unlocking process begins by analyzing the microprocessor’s architecture to identify how encryption is applied to the flash memory. Specialized tools are used to break through these security layers, allowing access to the program stored within the MCU. Once decoded, the firmware can be restored, allowing developers to replicate, repair, or modify the software for specific applications.
Unlocking the STM32F100VC flash program can be valuable for various purposes, such as cloning the firmware for use in new devices, recovering lost data, or restoring a malfunctioning system. In cases where the original program is no longer available, this process enables engineers to create backups or make modifications to the firmware without starting from scratch.

However, it’s important to recognize that MCU unlocking must be done within the confines of legal and ethical boundaries. Unauthorized access or duplication of the software could violate intellectual property rights. Therefore, professionals must always ensure that they have permission to perform flash program unlocking and adhere to applicable laws and regulations.
The independent watchdog is based on a 12-bit downcounter and 8-bit prescaler. It is clocked from an independent 40 kHz internal RC and as it operates independently of the main clock which can be useful for MCU STM32F100VC Flash Program Unlocking, it can operate in Stop and Standby modes.

It can be used either as a watchdog to reset the device when a problem occurs, or as a free-running timer for application timeout management before STMicroelectronics ST62T28 Memory Program Unlocking. It is hardware- or software-configurable through the option bytes. The counter can be frozen in debug mode.
The window watchdog is based on a 7-bit downcounter that can be set as free-running. It can be used as a watchdog to reset the device when a problem occurs. It is clocked from the main clock. It has an early warning interrupt capability and the counter can be frozen in debug mode by Recover AVR Chip ATMEL ATTINY15.
This timer is dedicated for OS, but could also be used as a standard downcounter. It features:
• A 24-bit downcounter
• Autoreload capability
• Maskable system interrupt generation when the counter reaches 0
• Programmable clock source
Up to two I²C bus interfaces can operate in multimaster and slave modes. They can support standard and fast modes. They support dual slave addressing (7-bit only) and both 7/10-bit addressing in master mode to support the process of Extract MCU PIC18F2431 Program. A hardware CRC generation/verification is embedded. They can be served by DMA and they support SM Bus 2.0/PM Bus.
One of the USART interfaces is able to communicate at speeds of up to 4.5 Mbit/s. The other available interfaces communicate at up to 2.25 Mbit/s. They provide hardware management of the CTS and RTS signals for the purpose of Crack Microcontroller ST7FMC1K6B6 Flash Program Memory, IrDA SIR ENDEC support, are ISO 7816 compliant and have LIN Master/Slave capability. All USART interfaces can be served by the DMA controller from Reverse Engineering Microcontroller.

