DSP Processor TMS320F2401AVFA Program Cloning
DSP Processor TMS320F2401AVFA Program Cloning needs to have a clear mind about all of the input and output ports defintion, since each one of the I/O ports has the specific function and usage of their own:
The F2401 has a total of 28 pins shared between primary functions and I/Os. These pins are divided into two groups:
Group1 — Primary functions shared with I/Os belonging to dedicated I/O ports, Port A, Port B, and Port C.
Group2 — Primary functions belonging to peripheral modules which also have a built-in I/O feature as a secondary function (for example, SCI, SPI, external interrupts, and PLL clock modules).
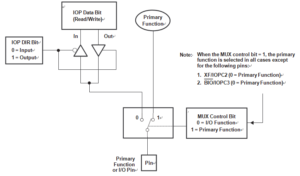
The control structure for Group1 type shared I/O pins is shown in below Figure. The only exception to this configuration is the CLKOUT/IOPC1 pin. In below Figure, each pin has three bits that define its operation:
Mux control bit — this bit selects between the primary function (1) and I/O function (0) of the pin.
I/O direction bit — if the I/O function is selected for the pin (mux control bit is set to 0), this bit determines whether the pin is an input (0) or an output (1).
I/O data bit — if the I/O function is selected for the pin (mux control bit is set to 0) and the direction selected is an input, data is read from this bit; if the direction selected is an output, data is written to this bit.
The mux control bit, I/O direction bit, and I/O data bit are in the I/O control registers.
DSP Processor TMS320F2401AVFA Program Cloning