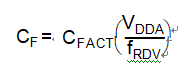Decrypt MC68HC11K4 Chip Encrypted Code
The external filter capacitor CF is critical to the stability and reaction time of the PLL. The PLL is also dependent on reference frequency and supply voltage which can easily being affected by Decrypt MC68HC11K4 Chip Encrypted Code process. The value of the capacitor must, therefore, be chosen with supply potential and reference frequency in mind. For proper operation, the external filter capacitor must be chosen according to the following equation:
For the value of VDDA, the voltage potential at which the MCU is operating should be used. If the power supply is variable, choose a value near the middle of the range of possible supply values.
This equation does not always yield a commonly available capacitor size, so round to the nearest available size. If the value is between two different sizes, choose the higher value for better stability. Choosing the lower size may seem attractive for acquisition time improvement, but the PLL may become unstable. Also, always choose a capacitor with a tight tolerance (±20% or better) and low dissipation.
Also important is the operating voltage potential applied to VDDA. The power supply potential alters the characteristics of the PLL. A fixed value is best. Variable supplies, such as batteries, are acceptable if they vary within a known range at very slow speeds. Noise on the power supply is not acceptable, because it causes small frequency errors which continually change the acquisition time of the PLL.
Temperature and processing also can affect acquisition time because the electrical characteristics of the PLL change. The part operates as specified as long as these influences stay within the specified limits. External factors, however, can cause drastic changes in the operation of the PLL. These factors include noise injected into the PLL through the filter capacitor, filter capacitor leakage, stray impedances on the circuit board, and even humidity or circuit board contamination.