Microchip Processor PIC16F1454 Data Memory Cracking
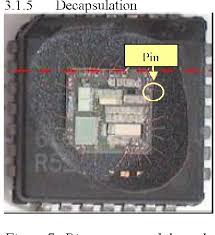
Microchip Processor PIC16F1454 Data Memory Cracking starts from decapsulate the silicon package of MCU PIC16F1454, get access to the internal security fuse bit of Microcontroller by focus ion beam and copy the firmware out from its memory which will help to recover microcontroller PIC16F1454 code;
The PIC16F1454 memory is broken into two sections: program memory and configuration memory. Only the size of the program memory changes between devices, the configuration memory remains the same:
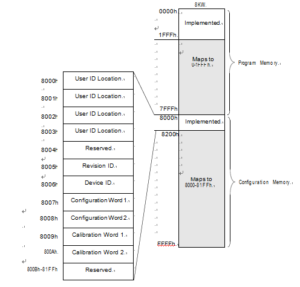
A user may store identification information (user ID) in four designated locations. The user ID locations are mapped to 8000h-8003h. Each location is 14 bits in length. Code protection has no effect on these memory locations. Each location may be read with code protection enabled or disabled like cracking ATmega2561 MCU heximal.

MPLAB® IDE only displays the seven Least Significant bits (LSb) of each user ID location, the upper bits are not read. It is recommended that only the seven LSbs be used if MPLAB IDE is the primary tool used to read these addresses which is similar to PIC18F2520 MCU code unlocking.
The Revision ID word is located at 8005h. This location is read-only and cannot be erased or modified. There are two Configuration Words, Configuration Word 1 (8007h) and Configuration Word 2 (8008h). The individual bits within these Configuration Words are used to enable or disable device functions such as the Brown-out Reset, code protection and Power-up Timer.

The internal calibration values are factory calibrated and stored in Calibration Words 1 and 2 (8009h, 800Ah). The Calibration Words do not participate in erase operations. The device can be erased without affecting the Calibration Words.

