Microcontroller Introduction
At present, Microcontroller penetrates into various fields of our lives, and it is almost difficult to find which field has no trace of the microcontroller. Small to phone, toy, mobile phone, all kinds of credit card machines, computer keyboards, color TVs, refrigerators, air conditioners, induction cookers, large cars, industrial automation, robots, missile navigation devices, and even the US Mars rover, these devices contain One or more microcontrollers. The number of microcontrollers is not only far more than PCs, even more than the number of humans. Therefore, the learning, development and application of microcontroller will create a large number of software and hardware engineers.
What is required to learn the microcontroller? Analog circuit, digital circuit foundation, have a certain understanding of C language or assembly language. Of course, these can also be mastered in the learning process. This set of tutorials are explained.
Hardware conditions: one computer, one set of experimental development platform.
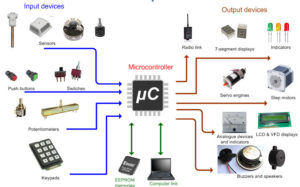
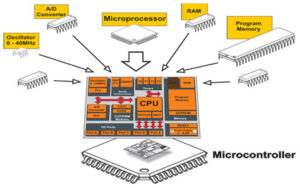
A working microcontroller must have several parts: CPU (operation, control), RAM (data storage – memory), ROM (program storage), input / output devices (for example: serial port, parallel output Mouth, etc.). These parts are divided into a number of chips on a personal computer and a printed circuit board called a motherboard is mounted. In the Microcontroller, these parts are all implemented in an integrated circuit chip, so it is called a MCU.
A microcontroller is a control chip, a tiny computer, and a crystal oscillator, a memory, an address latch, a logic gate, a seven-segment decoder (display), a button (similar to a keyboard), an expansion chip, an interface, etc. system.