Crack MC68HC705J1 Microcontroller Memory
A security feature discourages unauthorized reading of FLASH which can be viewed as Crack MC68HC705J1 Microcontroller Memory, its locations while in monitor mode. The host can bypass the security feature at monitor mode entry by sending eight security bytes that match the bytes at locations $FFF6–$FFFD. Locations $FFF6–$FFFD contain user- defined data.
Do not leave locations $FFF6–$FFFD blank. For security reasons, program locations $FFF6–$FFFD even if they are not used for vectors.
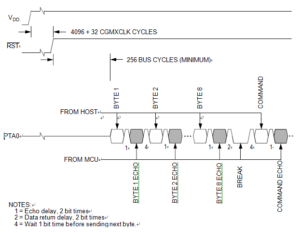
During monitor mode entry, the MCU waits after the power-on reset for the host to send the eight security bytes on pin PTA0. If the received bytes match those at locations $FFF6–$FFFD, the host bypasses the security feature and can read all FLASH locations and execute code from FLASH through MC68HC711PH8 Microcontroller Eprom Software Duplication. Security remains bypassed until a power-on reset occurs. If the reset was not a power-on reset, security remains bypassed and security code entry is not required. (See below Figure)
Upon power-on reset, if the received bytes of the security code do not match the data at locations $FFF6–$FFFD, the host fails to bypass the security feature. The MCU remains in monitor mode, but reading a FLASH location returns an invalid value and trying to execute code from FLASH causes an illegal address reset by Crack MC68HC705J1 Microcontroller Memory. After receiving the eight security bytes from the host, the MCU transmits a break character, signifying that it is ready to receive a command.
To determine whether the security code entered is correct, check to see if bit 6 of RAM address $50 is set. If it is, then the correct security code has been entered and FLASH can be accessed by Motorola M68HC711KA4 Flash Memory Replication.
The MCU does not transmit a break character until after the host sends the eight security bits. If the host fails the security bypass as described in 10.5 Security, the MCU remains in monitor mode, but reading a FLASH location returns an invalid value and trying to execute code from FLASH causes an illegal address reset after MCU Recovering. The MCU monitor commands are still valid and user software can execute from RAM. A bulk-erase operation is possible, erasing the entire FLASH memory, including the security bytes at $FFF6–$FFFD.